Search engine optimization (SEO) is inextricably linked to digital marketing. So if you’re interested in the field, it pays to understand the basics of SEO. SEO experts broadly categorize it into on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and technical SEO.
This article will dive into what on-page SEO is, why it matters, and how to use SEO tools to optimize your pages. If you’re new to SEO or looking to understand on-page SEO better, this guide is for you.
Feel free to use the clickable menu to skip ahead to any section that interests you:
- What is on-page SEO?
- Why is on-page SEO important?
- How to create SEO content
- How to optimize your SEO content
- Useful on-page SEO tools
- On-page SEO: FAQs
- Wrap-up
1. What is on-page SEO?
On-page SEO is the process of optimizing a webpage for search engine rankings which, in turn, enables the page to gain more website traffic. As the name implies, it includes changes to the page’s content and HTML to increase the search engine result ranking potential.
Because it’s page-based only, on-page SEO does not include off-page techniques, like getting backlinks to your website or building domain authority.
2. Why is on-page SEO important?
On-page SEO tells search engines a lot about the structure of your site and the content of your site’s pages.
For example, one aspect of on-page SEO is using titles and subheadings that include your main keyword. The title shows search engines that your post is likely to match certain search phrases, while the subheadings indicate how much of the topic you’ve covered in the post.
Having good on-page SEO assures search engines that your website has high-quality content that is worth ranking highly. On the other hand, poor on-page SEO can impact your site’s rankings negatively.
That said, it’s crucial to create content with SEO in mind.
3. How to create SEO content
Creating SEO content can be intimidating if the concept is new to you, but once you understand the basics, it can easily become second nature. Do these three things if you want to create content that appeals to search engines:
1. Conduct keyword research
The first, non-negotiable step toward creating SEO content is to find out what terms your audience is searching using search engines. That is the essence of keyword research.
Keyword research involves using SEO tools to discover which words and phrases your target audience are searching, how many users search for these keywords every month, and what your competitors have already written on the matter.
You can use several keyword research tools like Ahrefs Keyword Explorer (my favorite), Semrush, Uber Suggest, Moz Keyword Explorer, and Keyword Surfer. Keyword tools can help you find relevant keywords in your industry to target. You can also use them to research the keywords you already have on your radar.
Say you wanted to write about “how to become a freelance writer,” for example. Searching this keyword on Ahrefs keyword explorer would show you how easy (or hard) it would be to rank for it. You’d also see specific questions people are asking about the subject, as well as an estimate of how many people search for the keyword every month.
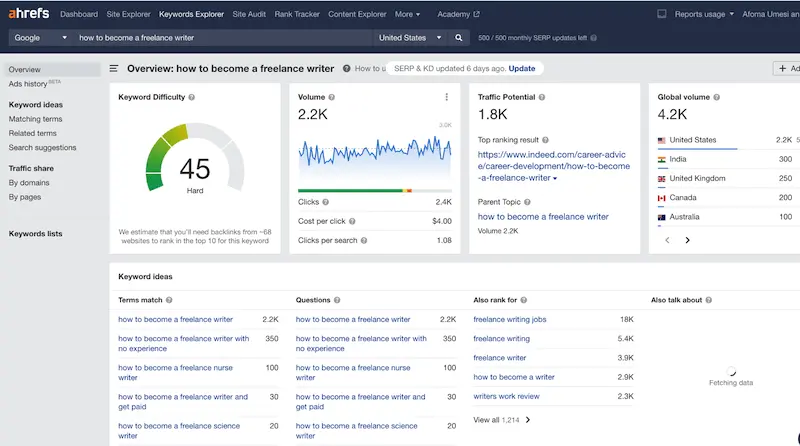
The information from keyword research can help you decide which keywords are worth pursuing and what you’ll need to include to cover them thoroughly.
2. Match search intent
Even with knowledge of relevant keywords, writers can fall into the trap of writing solely for search engines—without considering their audience. Creating useful content starts with matching search intent. Matching search intent means that you answer the readers’ questions (preferably, at the start of the article).
For example, this article is about on-page SEO. Hence, the first subheading tackles that right away. The article doesn’t begin with a long thesis about the history of SEO, then eventually circling back to on-page SEO. We’re also answering additional adjacent questions and showing you how to optimize your pages for search engines. That’s how to match search intent.
When you match search intent and optimize for search engines (more on that soon), you’ll get posts that rank higher and that are also useful for readers. When readers stay longer on your web pages and share your content on social media or with peers, it signals to search engines that your content is high-quality. This, in turn, leads to higher rankings.
3. Site structure and post structure
Subheadings aren’t just for aesthetics. They tell search engines about the scope of your article and can improve your rankings if done right. The same applies to your website structure—the categories on your site and the way posts and pages are organized.
For instance, if in your article about “how to become a freelance writer” but you never use the subheading with your keywords, your post is unlikely to rank. So even if you’ve written an informative post, but haven’t used your subheadings properly, few people will find your article on search engine result pages.
You should also use the right heading hierarchy. Experts agree that H1s should be reserved for the post title. Subsequent header tags can then be used after—H2, H3, and so on. While this doesn’t provide a direct SEO benefit, it makes your content easier to read and crawl, making it more likely to rank on search engines—assuming you’ve written valuable content in the first place.
4. How to optimize your SEO content
Once you’ve written (or made a plan to write) SEO content, it’s time to start optimizing it. Here are three things you must do to optimize your content for search engines:
Include your keyword
While there’s no specific formula for how often your keyword should show up in your piece, experts agree on one thing: your article should contain your keyword. Naturally, when you write about a topic, you’ll probably mention the theme or related words a few times throughout the piece—without trying.
What you should avoid, however, is a practice known as “keyword stuffing.” This is when keywords are squeezed into an article—even in unnatural-sounding ways—just to complete some mental quota of mentions. Search engines like Google can penalize your website for keyword stuffing.
Add internal links
Another under-appreciated on-page SEO best practice is internal linking. This refers to linking to other pieces of content on your site. For example, you’ll notice that many of our blog posts feature related articles in the “further reading” section. That’s an example of internal linking.
Internal links help your website by:
- Keeping readers on your site, hopping from one piece of content to the next
- Helping search engines understand how your site is organized
- Building authority for newer pages and articles on your site
The most effective internal links are links to related content—with descriptive anchor text. Readers are more likely to click on them, and search engines will be able to decipher them easily too.
Use images and alt-text
Images can be a powerful on-page SEO element. They can rank on search engine visual searches and can be discovered more readily than the articles themselves. Additionally, images break up text-heavy pieces and can make articles more enjoyable. Some types of images (like infographics) are also easier to share and can make your content more popular.
To make the best of images as an on-page SEO component you should add descriptive alt-text, preferably containing your post keyword. Alt-text helps improve your website’s accessibility and can help visually impaired people benefit more from reading your content.
Other things to do for image SEO optimization are:
- Choosing an image that complements your text
- Using a relevant image name (preferably with your keyword)
- Resizing and optimizing images so they load faster (which improves on-page SEO)
- Adding images to your site’s XML sitemap
- Including captions, if applicable, to help readers benefit from your image
We’ve considered many things to do if you want to create SEO content, but as you may have noticed, many of these things require tools for execution.
5. Useful on-page SEO tools
SEO in general requires a few essential tools if you want to do a solid job. On-page SEO is no different.
Google Search Console
This Google tool helps you get your site on Google search engine results pages, monitor traffic, identify serious site issues, and see which keywords bring in the most traffic. You can submit URLs for crawling and submit sitemaps to help your site rank faster.
Ahrefs Keyword Explorer
Ahrefs, which we mentioned earlier, is an all-in-one SEO tool for keyword research, competitor gap analysis, website SEO audit, and much more. You can also monitor your website for internal linking issues or page errors, see which content is ranking highest in your industry, and analyze your competitors’ content.
Some SEO experts prefer Semrush (another all-inclusive SEO tool) to Ahrefs.
Clearscope
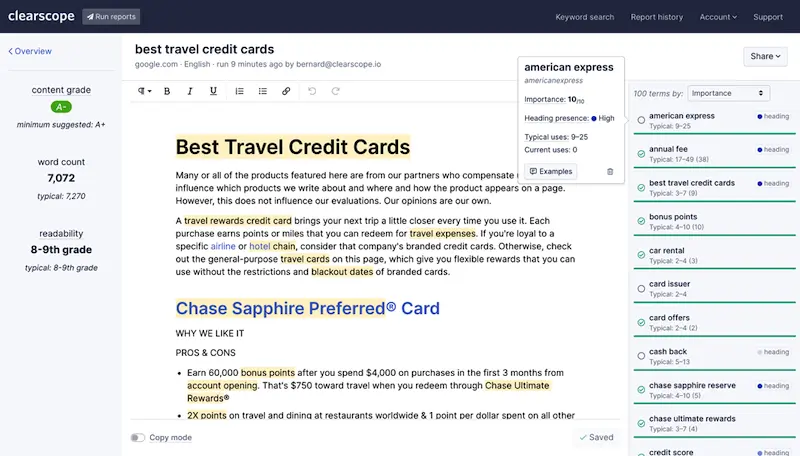
Clearscope is an artificial intelligence SEO tool that helps you create content to match search intent. It evaluates the highest ranking content for your keyword and provides a set of relevant key phrases to guide you as you create content. It then scores your piece relative to competing content.
Frase.io is a cheaper Clearscope alternative.
Google Developers PageSpeed Insight
One crucial on-page SEO factor we haven’t mentioned yet is site speed. Slow websites can frustrate users, increase bounce rates and signal to search engines that your site is not a high-quality resource. This Google tool evaluates your site’s page speed and provides suggestions on how to improve it.
Check out more of our top SEO tools in this post about 11 SEO tools you should know.
6. On-page SEO: FAQs
What is the most important on-page SEO factor?
There is no single most important factor. Most elements will not work without the others. You can write great content, but if your keyword isn’t in the title or meta description, it likely won’t rank. The basic things to learn for on-page SEO are:
- Writing to match search intent
- Optimizing titles, meta descriptions, and headings
- Adding relevant images with alt-text
Start here and you can add on other things later.
How can I learn on-page SEO?
By reading articles like this! If you want something more in-depth, I recommend Ahrefs SEO course. Ahrefs is one of the best in the game; there’s no better company to learn from.
What is an example of on-page SEO?
Examples of on-page SEO include headings and subheadings, internal linking, and images and alt-text. These are all elements on the page that, when optimized, can help your website content rank higher on search engines—and drive more traffic.
7. Wrap-up and further reading
On-page SEO is crucial for a successful website with high search engine rankings. Although it can sound like gibberish in the beginning, with a little research, SEO is easier to implement. The key to great SEO content is serving your readers.
Use headings and subheadings that provide content structure, add images to make content more appealing, and include your keyword naturally throughout the text to signal relevance to search engines.
Interested in SEO and digital marketing? Why not check out our free, 5-day short course, or check out these articles:
