Agile is the way forward.
But is it possible for every organization to work that way? When thinking of Agile product management, you might think of a small team huddled together, working on an idea, creating output fast.
However, when thinking of large organizations or enterprises, you might rather think of processes being slow and bureaucratic.
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) provides a way for large organizations to implement Lean-Agile practices. Thus making it possible to work more time and cost efficiently, as well as customer centric and to put a focus on team collaboration.
In this guide, you’ll learn what SAFe is, the core principles it’s based on and what benefits it has.
We’ll cover the following:
- What is SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework)?
- Benefits of using SAFe
- How product managers use SAFe
- Scaled Agile Framework FAQs
1. What is the Scaled Agile Framework?
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) is widely used within large organizations to manage complex projects over multiple teams and departments.
As the name already indicates, SAFe is a framework that implements Agile practices on a large scale, where Scrum or Kanban alone are not enough anymore. SAFe provides an efficient way of aligning teams, improving collaboration, managing dependencies, and delivering value to the customers.
Scaled Agile Framework principles
In order to achieve its aims, SAFe offers a comprehensive set of principles. These are set out in great detail on the official SAFe website, but I’ll summarize them for you here:
Take an economic view
Maximize value while trying to keep development time as short as possible.
Apply systems thinking
A person or a team is not operating within a vacuum, but is part of a larger system. Therefore, one should always consider how their work affects the rest of the system.
Assume variability; preserve options
Instead of committing to one design option and a set of requirements early on in the development process, it’s encouraged to work with several design options and requirements for a while and let empirical data help with the final decision.
Build incrementally with fast, integrated learning cycles
Working in short intervals (such as sprints) guarantees fast output and therefore fast customer feedback. This feedback can then quickly be integrated, using prioritization models such as Weighted Shorted Job First (WSJF).
Base milestones on objective evaluation of working systems
There should be set points of evaluation throughout the development cycle, to assess the solution that is being worked on. This is to minimize risk and maximize value.
Make value flow without interruptions
The processes within the development cycle should be as smooth as possible, in order to create a continuous flow of value to customers.
This includes for instance, limiting work in process, reducing bottlenecks, minimizing dependencies and getting faster feedback. Employing an Agile Release Train will really help with this.
Apply cadence, synchronize with cross-domain planning
Cadence means that the development cycle runs by a certain rhythmic pattern, which creates predictability within the process.
Predictability for everyone involved—the developers, management, stakeholders, and the customers. And synchronization across teams and departments is needed for alignment and risk reduction.
Unlock the intrinsic motivation of knowledge workers
An organization should create an environment for its employees where they can autonomously make decisions, since they know best about matters of their own work. This autonomy can then create space for innovation.
Decentralize decision-making
In order to deliver value increments fast, decision-making should be decentralized, meaning that decisions should be made on the spot, by the teams and individuals involved without escalating it to the level(s) above, so that delays can be avoided. However, when it comes to strategic decisions, the decision-making should be centralized.
Organize around value
Focus on the value that can be created for the customer, instead of focusing on functional expertise.
What are the four levels of SAFe?
SAFe 6.0 (the latest version of the framework) offers four different levels of configuration. This way organizations can decide which configuration fits best to their needs. The levels are as follows:
Essential
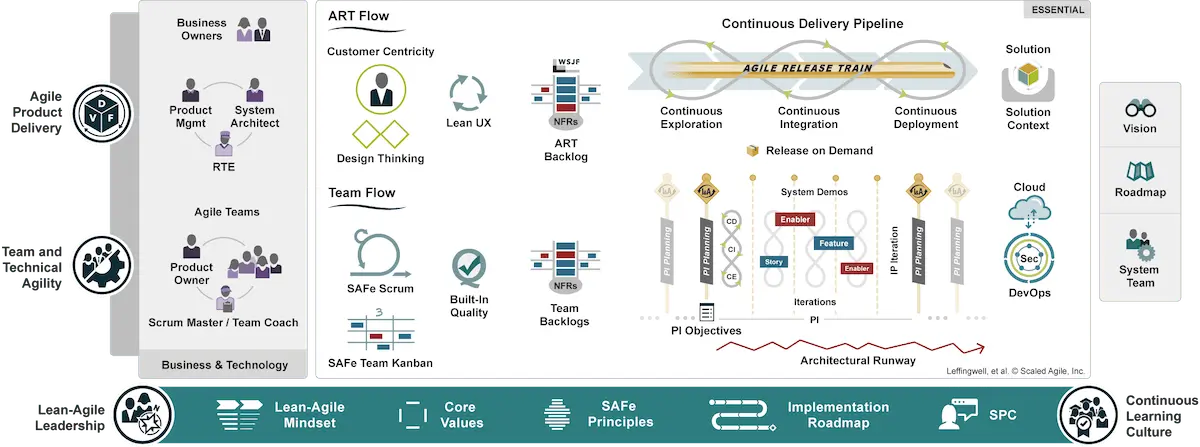
The Essential SAFe configuration is a common starting point for implementing SAFe within an organization. It focuses on managing multiple agile teams and projects.
Large Solution
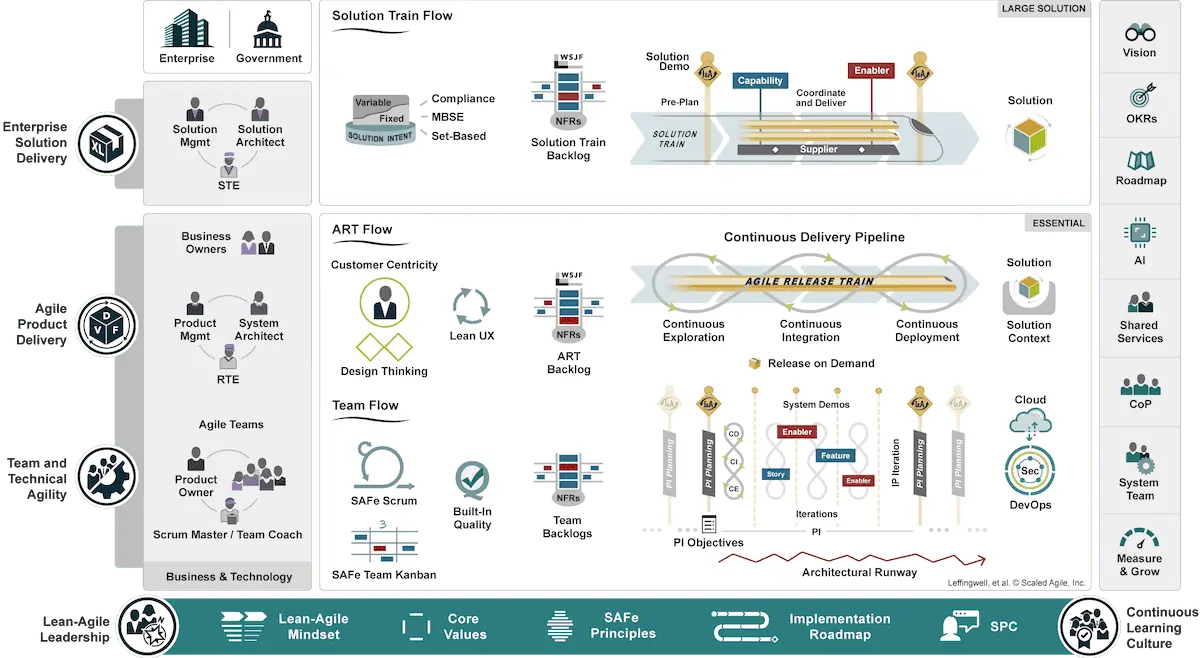
The Large Solution SAFe configuration offers a scaled-up version of the Essential configuration, meaning that even more teams and more complex projects/solutions can be managed. This configuration is meant for large enterprises.
Portfolio
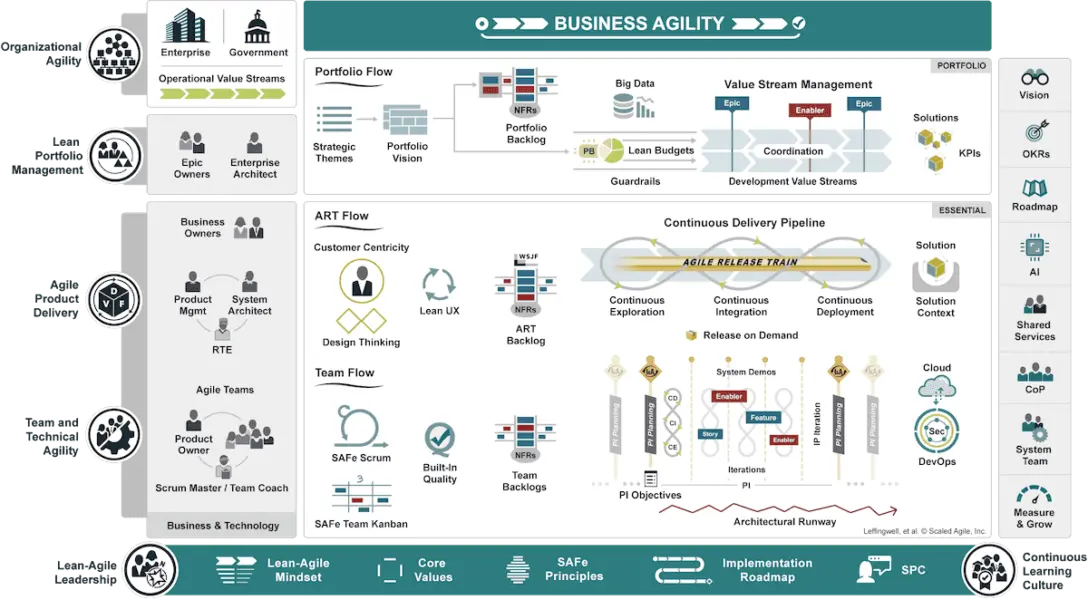
The Portfolio SAFe configuration offers portfolio management, high level strategic planning, and Lean budgeting.
Full
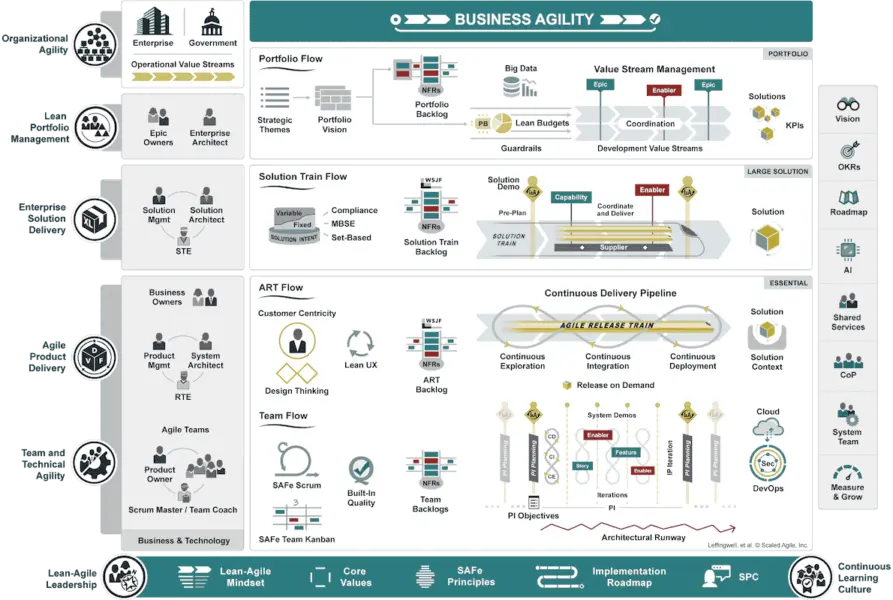
As the name suggests, the Full SAFe configuration offers all of the aforementioned configurations together and is thus the most comprehensive configuration.
2. Benefits of using SAFe
The most obvious benefit of the Scaled Agile Framework is its scalability, meaning that even big enterprises can use agile and lean practices and thus coordinate many teams and projects in a time and cost effective way.
Through SAFe, organizations are also able to quickly react to customer needs and market changes, which is important for customer satisfaction. Another benefit is the high level of transparency and collaboration between teams.
3. How product managers use SAFe
The Scaled Agile Framework differentiates between product management (as a more strategic department) and the role of Product Owner, who is part of an agile team and supports the implementation of the product strategy.
Let’s go through some of their respective responsibilities in more detail:
Product management:
- Exploring markets and users
- Connecting with customers
- Defining product strategy, vision and roadmaps
- Managing and prioritizing the backlog
- Delivering value
Product owner:
- Connecting with the customer
- Contributing to the vision and roadmap
- Managing and prioritizing the team backlog
- Supporting the team in delivering value
- Getting and applying feedback
This shows that product managers do have a place within SAFe, they just have to decide how they want to work. Would they prefer to work more strategically within the product management department, or more operationally, as a product owner.
4. Scaled Agile Framework FAQs
Let’s go through some of the most common questions relating to SAFe:
What is SAFe vs Agile?
Agile is an idea (or a set of principles) to work faster, more flexible, more efficiently, and at the same time customer-focused. SAFe is an agile framework, which implements these agile principles on a large scale within organizations.
It should also be mentioned that not everyone considers SAFe to be truly agile, since it takes quite some planning ahead in order to align a large number of teams efficiently. This means that flexibility and speed have to be compromised.
What is SAFe vs Scrum?
SAFe and Scrum are both agile frameworks. Scrum is used to manage a single team. The framework defines a team’s processes, responsibilities, roles and ways of collaboration. All of this is provided to work in a fast, flexible and customer-centric way.
SAFe on the other hand is a scaled framework, meaning it’s used if several agile teams need to work together. The bigger an organization gets, the harder it will be to continue working in a fast, flexible and at the same time customer-centred way, since there will have to be much more aligning between teams. SAFe offers a complex framework that allows big organizations to continue working in an agile way.
5. Final thoughts
The Scaled Agile Framework offers a viable solution for big organizations or enterprises to implement Lean-Agile practices and methodologies. It’s fair to say, though, that SAFe is a complex framework, which will take some time to learn and to implement.
As a beginner product manager it’s certainly worthwhile being aware of what is SAFe, its benefits and limitations, as well as where you can slot into it.
Do you want to learn more about product management? Then sign up for CareerFoundry’s free product management short course or check out some of the other guides:
